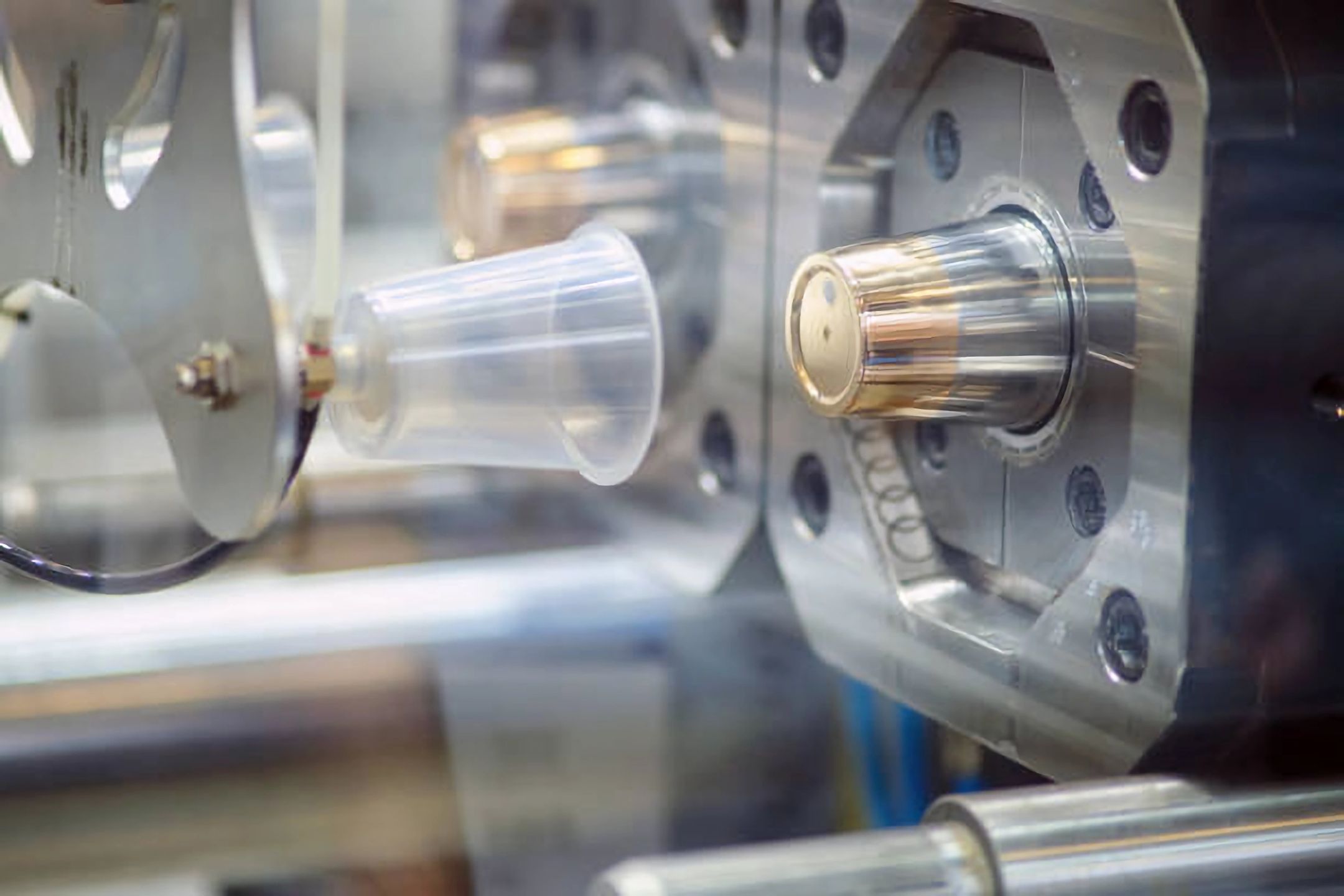
Unlock your product's potential with our One-stop solutions!
+86-755-83222882

GET QUOTE
What are the 3 Main Parts of the Injection Mold?
Injection molding is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, responsible for producing a vast array of plastic products. From household items to intricate automotive parts, plastic injection molding has revolutionized how we create durable and precise components. Central to this process is the injection mold itself, a sophisticated tool that shapes molten plastic into the desired form. Understanding the main parts of the injection mold is crucial for anyone involved in manufacturing or interested in the intricacies of this technology.
The Injection Mold
Injection molding involves injecting molten plastic into a mold, where it cools and solidifies into the final product. This process is highly efficient and capable of producing large volumes of identical items with remarkable precision. The injection mold is an essential component of this process, composed of several critical parts that work together to ensure the successful creation of plastic products.
The 3 Main Parts of the Injection Mold
While an injection mold can be complex and contain many components, three main parts are fundamental to its operation: the mold base, the mold cavity, and the mold core. Each part plays a specific role in the injection molding process, contributing to the production of high-quality plastic items.
The Mold Base
The mold base forms the foundation of the injection mold. It houses all the other components and provides the structural support necessary for the molding process. The mold base consists of several plates, including the clamping plate, cavity plate, core plate, and ejector plate. These plates are precisely machined to fit together seamlessly, ensuring the mold can withstand the high pressures and temperatures involved in plastic injection molding.
The clamping plate is where the mold attaches to the injection molding machine. This plate must be robust to handle the clamping force that keeps the mold closed during the injection process. The cavity and core plates, as their names suggest, contain the mold cavity and core, which shape the final product. The mold base also includes alignment features to ensure the mold closes correctly each time.
The Mold Cavity
The mold cavity is the hollow part of the mold where the molten plastic is injected. It is one of the most critical components of the injection mold, as it determines the shape and surface finish of the final product. The mold cavity is typically machined to precise dimensions to ensure that the plastic part produced matches the desired specifications exactly.
In a more complex injection mold, multiple cavities can be used to produce several parts in a single injection cycle, known as a multi-cavity mold. This capability significantly increases production efficiency and reduces manufacturing costs. The surface of the mold cavity can also be textured or polished to give the final product a specific finish, from glossy to matte, further enhancing its appearance and functionality.
The Mold Core
The mold core works in tandem with the mold cavity to shape the plastic product. While the cavity forms the external surfaces, the core shapes the internal features of the part. Together, they form a closed space into which molten plastic is injected. The design of the mold core is critical, as it must accommodate complex geometries and often includes intricate details that are vital to the functionality of the finished part.
The core and cavity are designed to fit together perfectly, with no gaps or misalignments, ensuring that the plastic product is produced accurately. Additionally, the core may contain channels for cooling to ensure that the molten plastic solidifies quickly and uniformly, minimizing defects and improving cycle times.
Supporting Components
Beyond the three main parts of the injection mold, several other components play vital roles in the plastic injection molding process. These include the runner system, the ejector system, and the cooling system.
Runner System
The runner system channels the molten plastic from the injection nozzle to the mold cavities. It includes runners, gates, and sprues, which must be designed to ensure a smooth flow of plastic without creating unnecessary waste or causing defects in the final product. The design of the runner system is crucial for maintaining the efficiency of the injection molding process. Hot runner systems, for instance, keep the plastic molten within the runner, reducing waste and improving cycle times.
Ejector System
Once the plastic has solidified, the ejector system removes the finished part from the mold. This system typically includes ejector pins, plates, and rods, which push the part out of the cavity without damaging it. The timing and force of the ejection must be carefully controlled to avoid deformation. Advanced molds may use air blasts or mechanical strippers in addition to ejector pins to ensure the part is released smoothly.
Cooling System
The cooling system is essential for controlling the temperature of the mold during the injection molding process. It typically involves a network of channels through which a cooling medium, such as water, circulates. Efficient cooling is crucial for maintaining consistent cycle times and ensuring the quality of the finished parts. Proper cooling design minimizes warping, reduces cycle time, and enhances the overall efficiency of the molding process.
Materials and Precision in Mold Making
Injection molds are typically made from durable materials such as hardened steel, pre-hardened steel, aluminum, and beryllium-copper alloy. The choice of material depends on factors like the production volume, type of plastic used, and the complexity of the mold. High-precision machining and sometimes even hand-finishing are required to create the mold components. This precision ensures that the mold can produce parts with tight tolerances and fine details.
The Future of Injection Molding
Looking ahead, the future of injection molding promises even greater advancements. Innovations such as 3D printing for mold making, more efficient cooling techniques, and enhanced automation are set to revolutionize the industry. These advancements will allow for more complex designs, faster production times, and even higher quality products. Staying informed about these trends and continuously improving mold design and manufacturing techniques will be crucial for anyone involved in the industry.
Conclusion
Plastic injection molding continues to be a vital manufacturing process, and the injection mold remains at its heart. As technology advances, the design and capabilities of these molds will only continue to improve, opening up new possibilities for innovation and production in countless industries. Whether you are a seasoned professional or a curious newcomer, appreciating the complexity and precision of injection molds is key to understanding the marvels of modern manufacturing.
If you're looking for expertise, SZOMK offers an unparalleled range of injection molding services. Specializing in both public mold enclosures and custom mold development, SZOMK can provide detailed 3D drawings, solve technical challenges, and assist in the design of product appearance and structure. Additionally, SZOMK offers extensive supply chain resources and information services. With a rich product line and professional, efficient service, SZOMK is your go-to partner for all your injection molding needs.